The judiciary additionally gives a mechanism for the resolution of disputes. The superior courts of Malaysia comprise the Federal Court which is the apex court the Court of Appeal and the High Court of Malaya and the High Court of Sabah and Sarawak.

Chapter 1 Introduction To Law And The Malaysian Legal System Ppt Video Online Download
The hierarchy of courts begins from the Magistrates Court Sessions Court High Court Court of Appeal and finally the Federal Court.

. The High Court Court of Appeal and the Federal Court are superior courts while the Magistrates Court the Court for Children and the Sessions Court are subordinate courts. The Judicial Appointments Commission was set up under the Judicial Appointments Commission Act 2009 JAC Act to assist the Prime Minister PM in advising the Yang diPertuan Agong YDPA on the appointment of judges of the Superior Courts and judicial commissioners including the appointments of the Chief Justice. These courts have unlimited civil jurisdiction and also in criminal matters besides matters related to the Islamic family law.
The Chief Justice Malay. S CJA 1964 states that the court of Appeal is an appellate court of the judiciary system in Malaysia and has jurisdiction to hear appeals against any High Court decision relating to criminal matters. The Constitution also sets up a Special Court for the Yang DiPertuan Agong YDPA and other Rulers.
28 rows The high courts in Malaysia are the third-highest courts in the hierarchy of courts after the Federal Court and the Court of AppealArticle 121 of the Constitution of Malaysia provides that there shall be two high courts of co-ordinate jurisdictionthe High Court in Malaya and the High Court in Sabah and Sarawak before 1994 the High Court in Borneo. The COA hears appeals of both Criminal and Civil decisions from the High Court. Some matters which a High court may hear are custody of children legitimacy of.
Outside the court hierarchy are the Syariah Courts Native Courts and Special Court which will not be discussed in this article. Glossary of Common Civil Litigation Terms Retrieved November. The only major difference between the Malaysian Superior Court Hierarchy and the Senior Courts Hierarchy of England and Wales is that in Malaysia we do not have a Crown Court.
Sessions Courts has the authority to decide on civil and criminal cases. It also has jurisdiction to try cases whose maximum penalty does not exceed 10. Article 121 of the Constitution provides for two High Cou.
These courts are vested with the original jurisdiction to. On the other hand the superior courts are. Malaysias Judicial System The Federal Court is Malaysias highest court.
One of the reasons is because the court system in Malaysia is practicing a judicial precedent. The COA has the final jurisdiction on criminal cases that starts from subordinate court. It should be noted that there is no jury system in Malaysia for criminal matters as it was effectively abolished.
Judicial Appointments Commission Selection Process and Method of Appointment of Judges of the Superior Courts Amendment Regulations 2021. Two High Courts one for Peninsular Malaysia known as the High Court in Malaya and one for Sabah and Sarawak known as the High Court in Sabah and Sarawak. Outside the court hierarchy are the Syariah Courts Penghulus Courts and the Native Courts.
The hierarchy of courts of Malaysia starts with the Magistrates Court as the first level followed by the Sessions Court High Court Court of Appeal and the Federal Court of Malaysia which is the highest level. Judges Code Ethics Act. It is the final court of appeal and has exclusive jurisdiction over constitutional issues as.
Malaysia has a bound together legal framework and. The High Court the Court of Appeal and the Federal Court. The Superior Courts Malaysian legal system hierarchy comprises the Malaysian High Court the Court of Appeal the Federal Court and the Court of Sarawak and Sabah.
Explain the jurisdiction of all the Superior Courts in Malaysia. High Court The High Court has general revisionary and supervisory jurisdiction over all Subordinate Courts and hears appeals related to criminal and civil cases from Subordinate Courts. JUDICIAL APPOINTMENTS COMMISSION Level 5 North Block Palace of Justice Precinct 3 62506 Putrajaya Malaysia.
The High Court Court of Appeal and the Federal Court are superior courts. The Superior Courts comprise the Federal Court the Court of Appeal and the two High Courts one for Peninsular Malaysia and one for Sabah and Sarawak formerly known as Borneo. What is the Judicial Appointments Commission.
These courts are referred to as the Superior Courts. There are 2 high courts in Malaysia which have revisionary and general supervisory jurisdiction over the subordinate courts. Judges Code of Ethics 2009.
The appointment of judges of Superior Court level is being set out under Article 122B of the the. Tel 03 8880 3545 3546 Fax 03 8880 3549 Email setiausahajacgovmy. The Sessions Courts have powers to hear all criminal matters except for offences punishable.
Judicial precedent is a previous judicial decision or preceding that may adopted by the judges. There are generally two types of trials criminal and civil. The criminal cases do not include cases involving the death penalty.
Superior Court Level The Superior Courts in Malaysia consist of the Federal Court the Court of Appeal and the High Courts. The Magistrate Court has jurisdiction to try civil cases whose claim does not exceed RM 25000. Ketua Hakim Negara is the head of the Malaysian judiciary and also the head of the Federal Court the highest court of Malaysia.
The Federal Court of Malaysia in the highest court of the land. Thursday 21 January 2010 1545 The Malaysian Courts of Justice are made up of the Superior Courts and the Subordinate Courts. The Magistrates Court the Court for Children and the Sessions Court are subordinate courts.
In civil matters also the court of Appeal has jurisdiction to hear and determine which stated in S1 CJA 1964. The two High Courts which are of co-ordinate jurisdiction further branch out into local jurisdictions. The judiciary which is also known as the judicial system or court system is the arrangement of courts that decodes and applies the law for the state.
The Sessions Courts hear all matters of which the claim exceeds RM25000-00 but does not exceed RM250000-00 except in matters relating to motor vehicle accidents landlord and tenant and distress where the Sessions Courts have unlimited jurisdiction. The jurisdiction of the courts in civil or criminal matters are contained in the Subordinate Courts Act 1948 and the Courts of Judicature Act 1964. No Mr Justice Peter cannot decline to be bound by the decision of Court of Appeal.

The Malaysian Court System Asklegal My

Hierarchy Portal Rasmi Pejabat Ketua Pendaftar Mahkamah Persekutuan Malaysia

Then Now Supreme Court Kl In The 1920 30 S To What Is Now The Ministry Of Tourism Culture Offices Old Photos Kuala Lumpur Tourism

Judicial Independence In South Korea Revisited

Role And Structure Of The Supreme Court Structure

Here S How You Could Attend Any Court Case In Malaysia Asklegal My

Court Of Appeal Dismisses Plea By Mother Of Malaysian Drug Trafficker On Death Row Cna
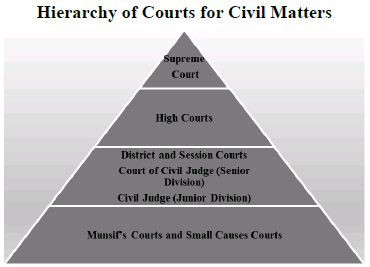
Hierarchy Of Courts For Civil Cases In India Civil Law India

Orange County Superior Court Linkedin

Malaysian Ex Pm Najib S 12 Year Jail Sentence Upheld In 1mdb Linked Case Says Appeal Court South China Morning Post

Malaysian Drug Trafficker On Death Row Tested Negative On Art Prior To Court Appearance Sps Cna

The Former City Hall Singapore Ferry Building San Francisco Singapore City Hall
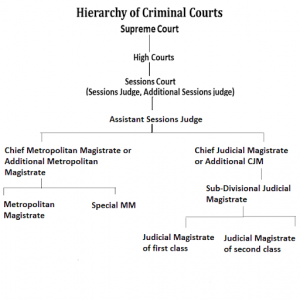
Criminal Courts Constitution Role Hierarchy Under The Crpc

Courthouse Kuala Lumpur Malaysia Kuala Lumpur Malaysia Ferry Building San Francisco
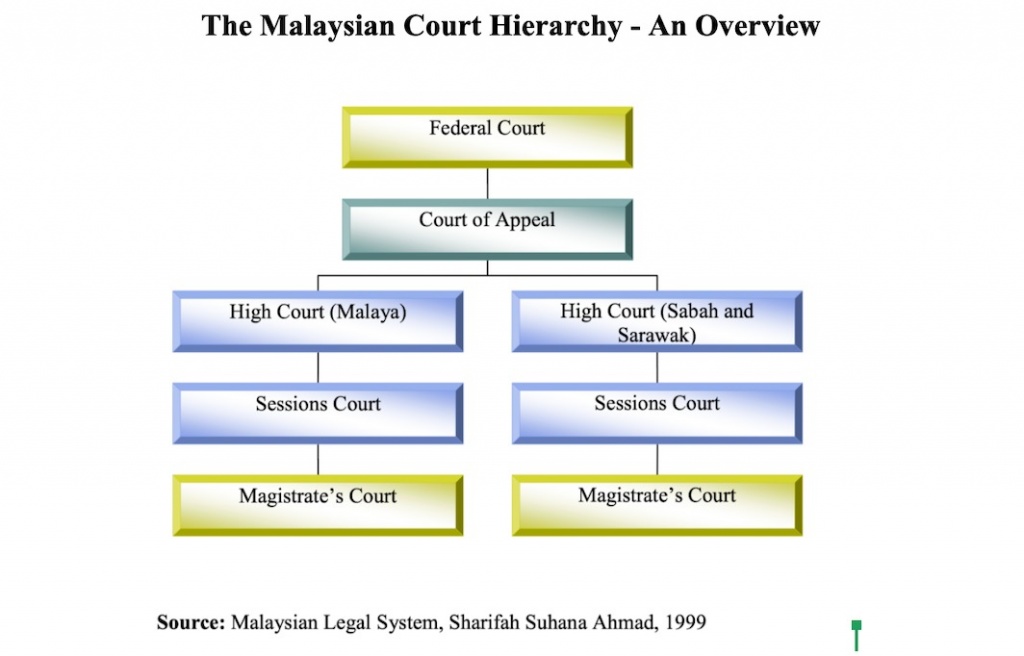
The Malaysian Court Hierarchy A Review Of Malaysia S Civil And Criminal Court Hierarchy Richard Wee Chambers

Stephanie Campbell Director Of The Office Of Sexual Health And Youth Development Massachusetts Department Of Public Health Linkedin

The Malaysian Court System Asklegal My

You Can Make An Appeal If You Lose Your Case In Asklegal My

Malaysia Standing International Forum Of Commercial Courts
